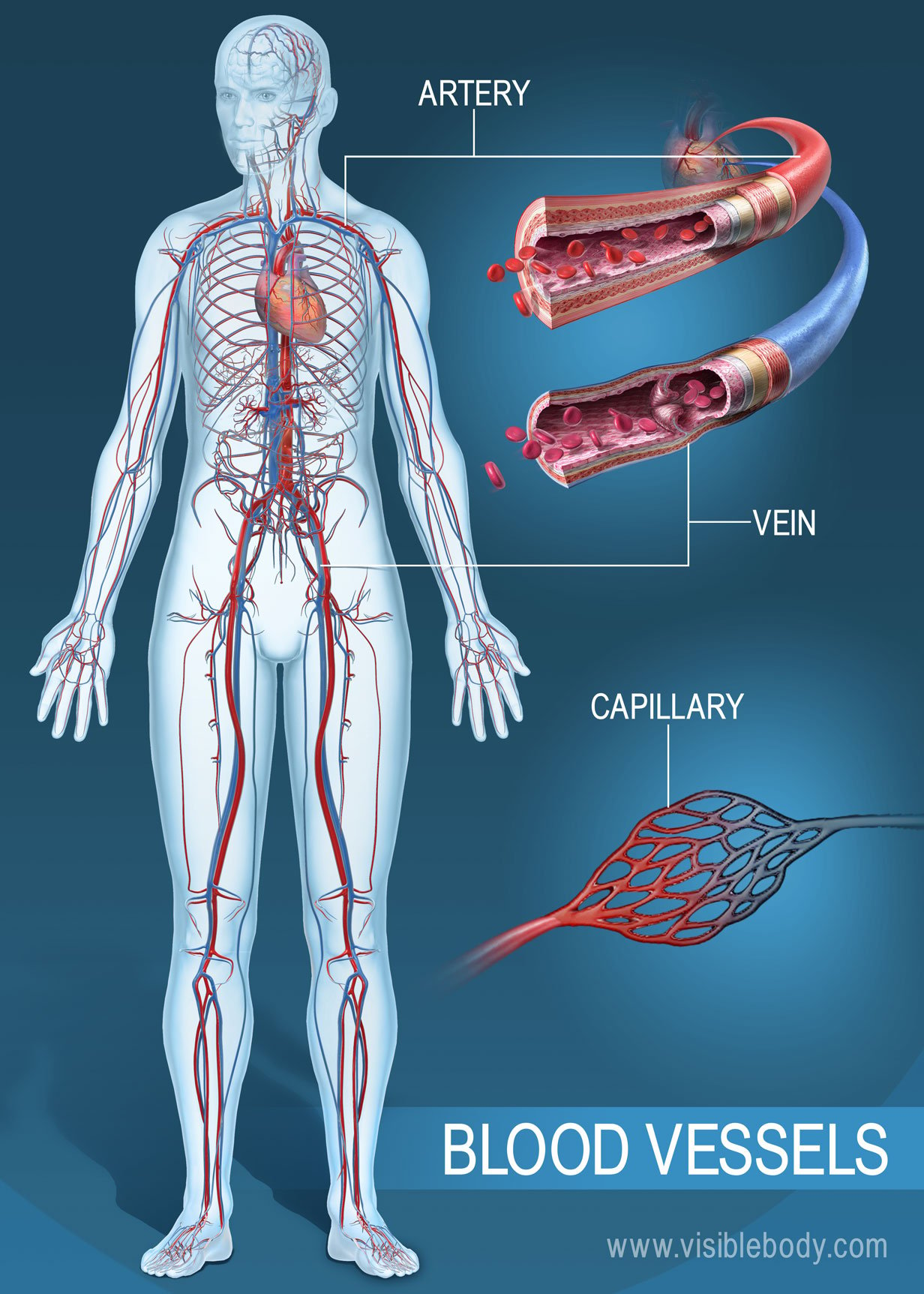
Figure 18.2.2 18.2. 2: Structure of Blood Vessels. (a) Arteries and (b) veins share the same general features, but the walls of arteries are much thicker because of the higher pressure of the blood that flows through them. (c) A micrograph shows a similarly sized artery and vein.
Vision and the eye’s anatomy | HealthEngine Blog
Medical Terminology Chapter 1. The surgical puncture of the abdominal cavity to remove fluid for diagnostic purposes. a word formed from the initial letters of the major parts of a compound term. A condition that has a rapid onset, a severe course, and a relatively short duration. The process of producing a radiographic study of the blood
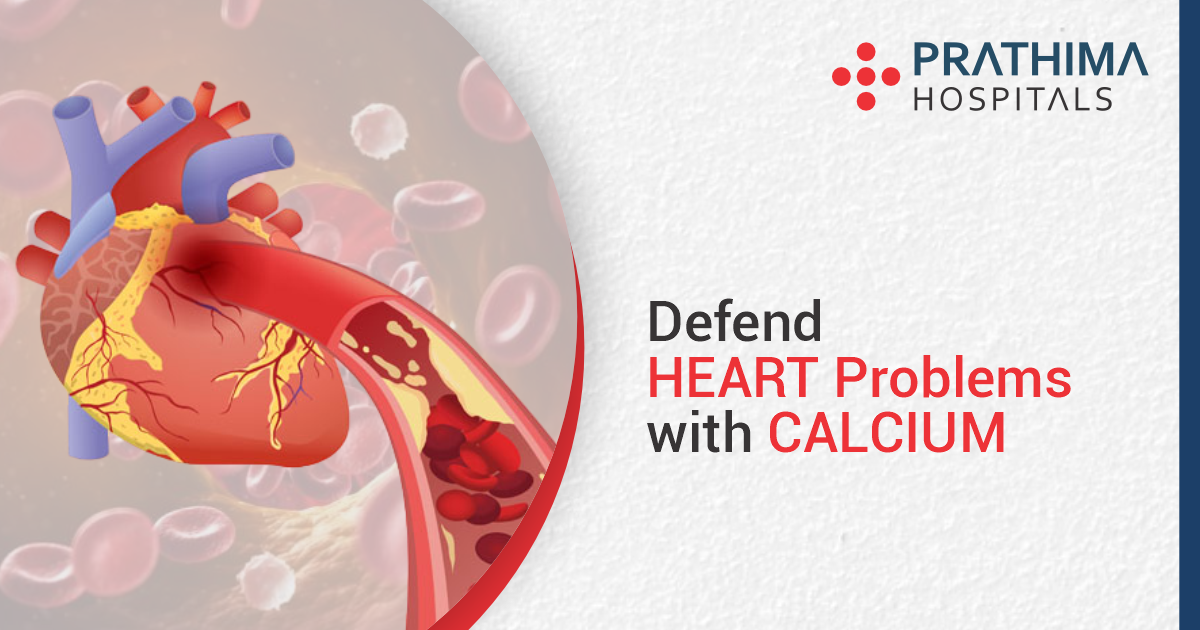
Source Image: prathimahospitals.com
Download Image
An artery is an elastic blood vessel that transports blood away from the heart. This is the opposite function of veins, which transport blood to the heart. Arteries are components of the cardiovascular system. This system circulates nutrients to and removes waste material from the cells of the body .
Source Image: visiblebody.com
Download Image
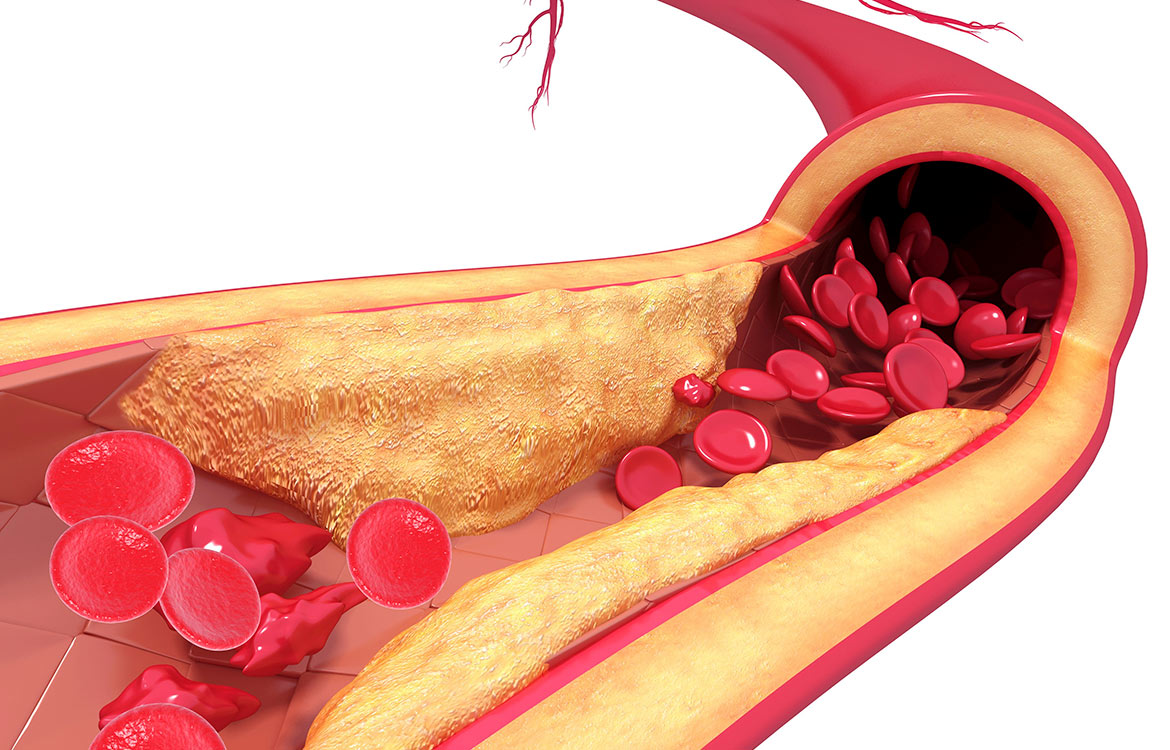
Fibrous Caps in Atherosclerosis Form by Notch-Dependent Mechanisms Common to Arterial Media Development | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology Atherosclerosis is thickening or hardening of the arteries caused by a buildup of plaque in the inner lining of an artery. Risk factors may include high cholesterol and triglyceride levels, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, obesity, physical activity, and eating saturated fats. Atherosclerosis can cause a heart attack, stroke, aneurysm

Source Image: pharmrev.aspetjournals.org
Download Image
Pertaining To The Interior Or Lining Of An Artery
Atherosclerosis is thickening or hardening of the arteries caused by a buildup of plaque in the inner lining of an artery. Risk factors may include high cholesterol and triglyceride levels, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, obesity, physical activity, and eating saturated fats. Atherosclerosis can cause a heart attack, stroke, aneurysm Nov 3, 2023This article will discuss the layers of the heart (the epicardium, the myocardium and the endocardium) and any clinical relations pertaining to them.. In the same way that vehicles have their fuel pumps, our body has the heart. The heart is a muscular organ found in the middle mediastinum that pumps blood throughout the body. It is housed in the pericardial sac, which protects it and assists
Endothelial Dysfunction in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases and Beyond: From Mechanism to Pharmacotherapies | Pharmacological Reviews
Endarterial (end-ar-TEE-ree-al) means pertaining to the interior or lining of an artery (end- means within, arteri means artery, and -al means pertaining to). ather/o means plaque or fatty substance. An atheroma (ath-er-OH-mah) is a fatty deposit within the wall of an artery (ather means fatty substance, and -oma means tumor). Atherosclerosis Prevention & Risk Factors: What to Know | MDVIP
Source Image: mdvip.com
Download Image
Heart attack Information | Mount Sinai – New York Endarterial (end-ar-TEE-ree-al) means pertaining to the interior or lining of an artery (end- means within, arteri means artery, and -al means pertaining to). ather/o means plaque or fatty substance. An atheroma (ath-er-OH-mah) is a fatty deposit within the wall of an artery (ather means fatty substance, and -oma means tumor).
Source Image: mountsinai.org
Download Image
Vision and the eye’s anatomy | HealthEngine Blog Figure 18.2.2 18.2. 2: Structure of Blood Vessels. (a) Arteries and (b) veins share the same general features, but the walls of arteries are much thicker because of the higher pressure of the blood that flows through them. (c) A micrograph shows a similarly sized artery and vein.

Source Image: healthinfo.healthengine.com.au
Download Image
Fibrous Caps in Atherosclerosis Form by Notch-Dependent Mechanisms Common to Arterial Media Development | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology An artery is an elastic blood vessel that transports blood away from the heart. This is the opposite function of veins, which transport blood to the heart. Arteries are components of the cardiovascular system. This system circulates nutrients to and removes waste material from the cells of the body .

Source Image: ahajournals.org
Download Image
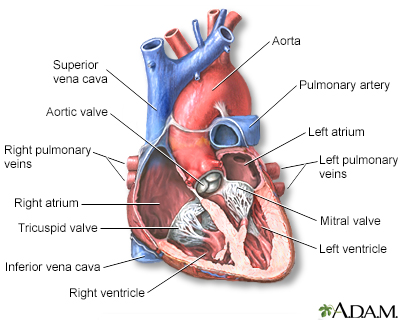
Causes and Implications of Coronary Artery Disease – TCI Hospital EN May 13, 2022Figure 20.1.1 20.1. 1: Cardiovascular Circulation. The pulmonary circuit moves blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs and back to the heart. The systemic circuit moves blood from the left side of the heart to the head and body and returns it to the right side of the heart to repeat the cycle.
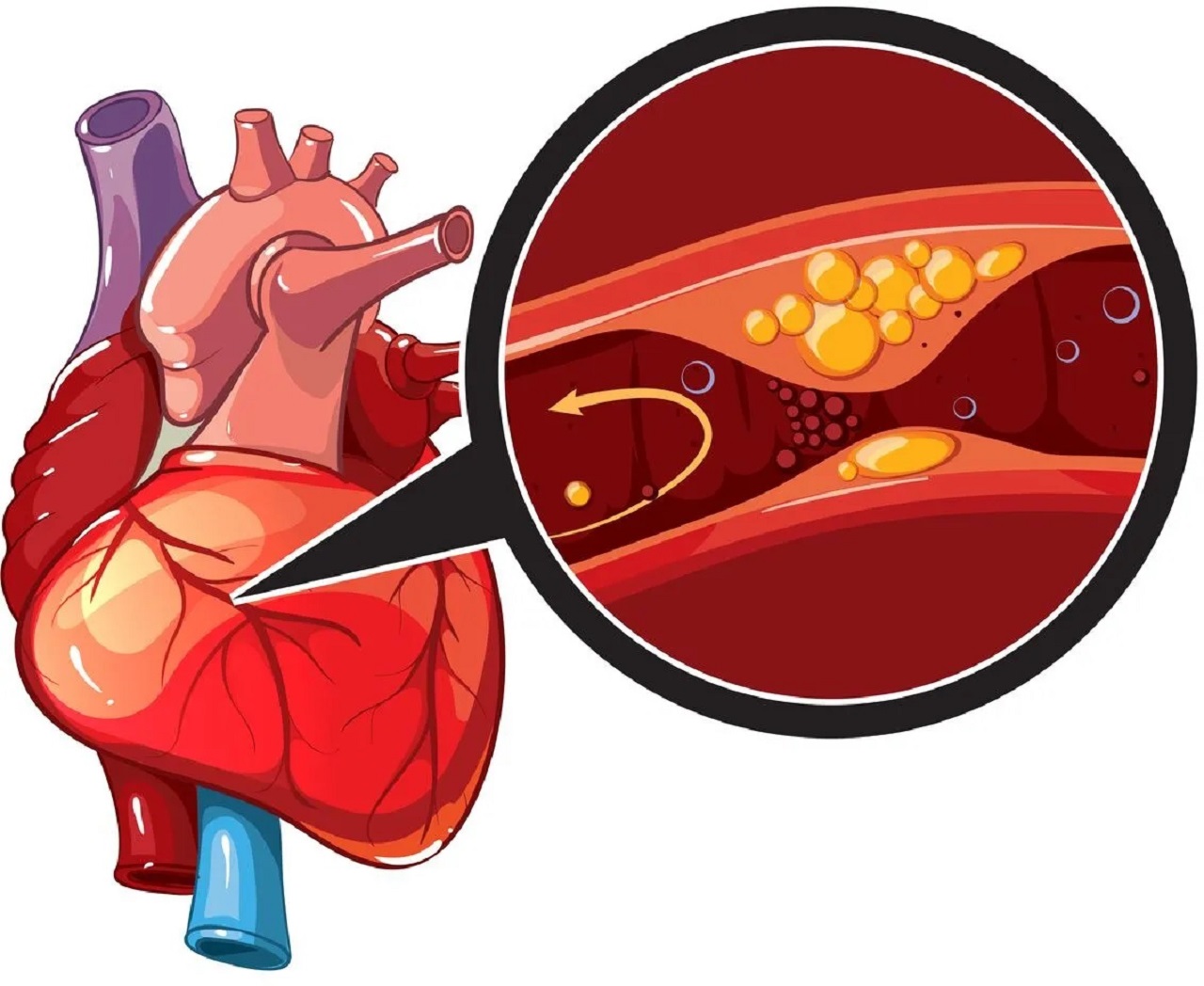
Source Image: en.benhvienthucuc.vn
Download Image
Elevated Plasmin(ogen) as a Common Risk Factor for COVID-19 Susceptibility | Physiological Reviews Atherosclerosis is thickening or hardening of the arteries caused by a buildup of plaque in the inner lining of an artery. Risk factors may include high cholesterol and triglyceride levels, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, obesity, physical activity, and eating saturated fats. Atherosclerosis can cause a heart attack, stroke, aneurysm

Source Image: journals.physiology.org
Download Image
What is ‘arthrosclerosis’? – Quora Nov 3, 2023This article will discuss the layers of the heart (the epicardium, the myocardium and the endocardium) and any clinical relations pertaining to them.. In the same way that vehicles have their fuel pumps, our body has the heart. The heart is a muscular organ found in the middle mediastinum that pumps blood throughout the body. It is housed in the pericardial sac, which protects it and assists
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Heart attack Information | Mount Sinai – New York
What is ‘arthrosclerosis’? – Quora Medical Terminology Chapter 1. The surgical puncture of the abdominal cavity to remove fluid for diagnostic purposes. a word formed from the initial letters of the major parts of a compound term. A condition that has a rapid onset, a severe course, and a relatively short duration. The process of producing a radiographic study of the blood
Fibrous Caps in Atherosclerosis Form by Notch-Dependent Mechanisms Common to Arterial Media Development | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology Elevated Plasmin(ogen) as a Common Risk Factor for COVID-19 Susceptibility | Physiological Reviews May 13, 2022Figure 20.1.1 20.1. 1: Cardiovascular Circulation. The pulmonary circuit moves blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs and back to the heart. The systemic circuit moves blood from the left side of the heart to the head and body and returns it to the right side of the heart to repeat the cycle.