This behavior is referred to as a “decaying” exponential function. The time τ (tau) is referred to as the “time constant” and can be used (as in this case) to indicate how rapidly an exponential function decays.. Here: t is time (generally t > 0 in control engineering); V 0 is the initial value (see “specific cases” below).; Specific cases. Let =; then =, and so =
The Rule of 70 » Darrin Qualman
The time is known to have an exponential distribution with the average amount of time equal to four minutes. X is a continuous random variable since time is measured. … The curve is: f(x) = 0.25e -0.25x where x is at least zero and m = 0.25. For example, f(5) = 0.25e −(0.25)(5) = 0.072. The postal clerk spends five minutes with the customers.

Source Image: infinityisreallybig.com
Download Image
The only difference is the value of the constant, k. Higher values of k lead, in a sense, to faster decay. To help emphasize this, we can define a constant: τ = 1/k. Then we can re-write the function this way: N (t) = N o e -t/τ. We call τ the “time constant” for this decay. It has the units of time. And it gives us an intuitive feeling
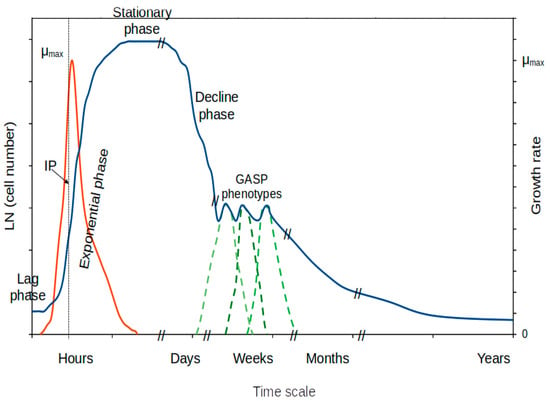
Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
How Populations Grow: The Exponential and Logistic Equations | Learn Science at Scitable
Into how many time constants is an exponential curve divided? Expert Solution Trending now This is a popular solution! Step by step Solved in 2 steps See solution Check out a sample Q&A here Knowledge Booster Learn more about Analysis of Multiple Order System and Steady State Error Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application?
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Into How Many Time Constants Is An Exponential Curve Divided
Into how many time constants is an exponential curve divided? Expert Solution Trending now This is a popular solution! Step by step Solved in 2 steps See solution Check out a sample Q&A here Knowledge Booster Learn more about Analysis of Multiple Order System and Steady State Error Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application?
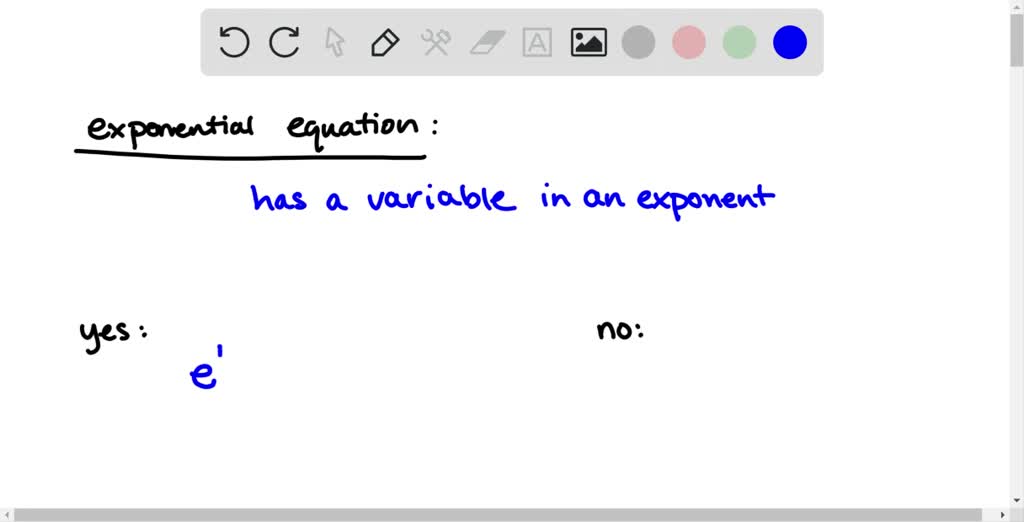
In an exponential function of the form f (x) = a*b^x, the initial value is usually taken to be the value of f (0), or “a”. The common ratio refers to the rate of change in an exponential function. In the form given above, the common ratio is “b”. For example, in the function f (x) = 2*3^x, the initial value is 2 and the common ratio is 3.
⏩SOLVED:Into how many time constants is an exponential curve… | Numerade
What electrical quantity does the oscilloscope measure? engineering. What type of meter contains its own separate power source? 1 / 4. Find step-by-step Engineering solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: Into how many time constants is an exponential curve divided?.
SOLVED: 9. Into how many time constants is an exponential curve divided?

Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Processes | Free Full-Text | Exponential Curve-Based Control Strategy for Auxiliary Equipment Power Supply Systems in Railways
What electrical quantity does the oscilloscope measure? engineering. What type of meter contains its own separate power source? 1 / 4. Find step-by-step Engineering solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: Into how many time constants is an exponential curve divided?.
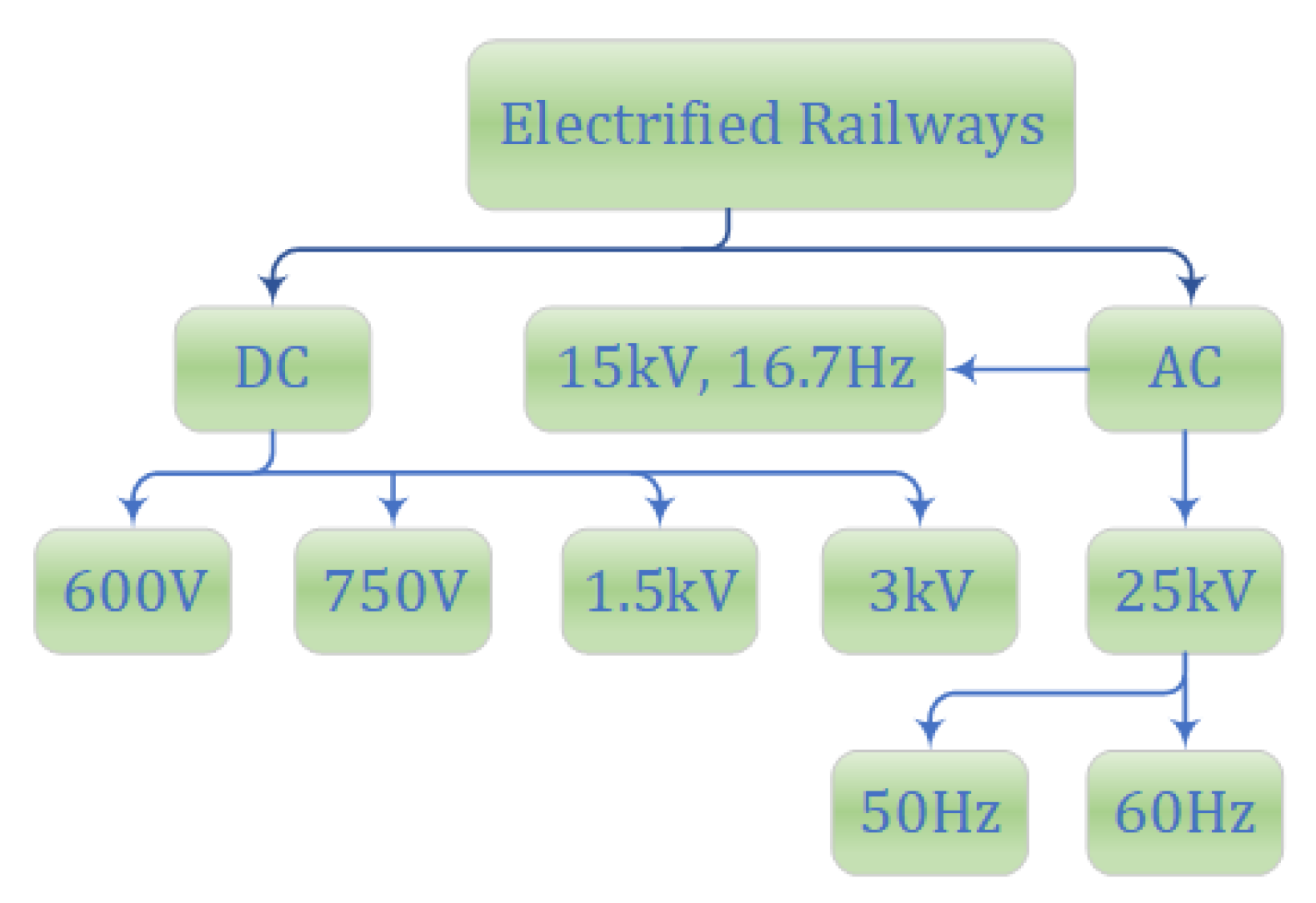
Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
The Rule of 70 » Darrin Qualman
The only difference is the value of the constant, k. Higher values of k lead, in a sense, to faster decay. To help emphasize this, we can define a constant: τ = 1/k. Then we can re-write the function this way: N (t) = N o e -t/τ. We call τ the “time constant” for this decay. It has the units of time. And it gives us an intuitive feeling
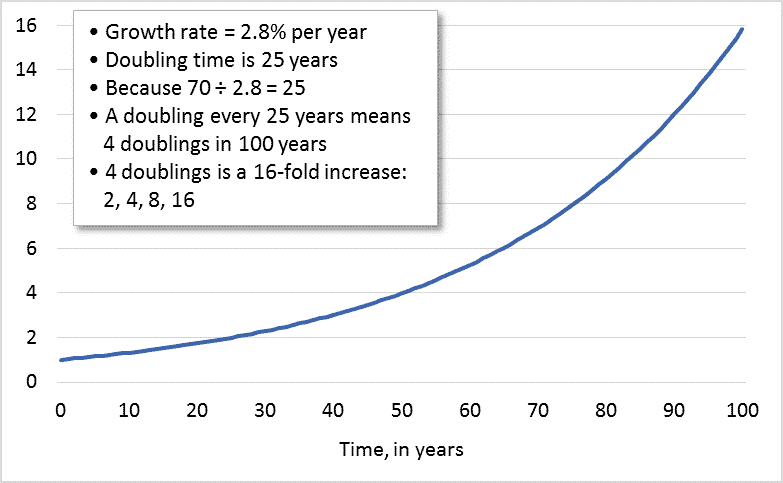
Source Image: darrinqualman.com
Download Image
How Populations Grow: The Exponential and Logistic Equations | Learn Science at Scitable
This behavior is referred to as a “decaying” exponential function. The time τ (tau) is referred to as the “time constant” and can be used (as in this case) to indicate how rapidly an exponential function decays.. Here: t is time (generally t > 0 in control engineering); V 0 is the initial value (see “specific cases” below).; Specific cases. Let =; then =, and so =

Source Image: nature.com
Download Image
Exponential Decay and Time Constants | Advanced Math for Young Students
Solutions for Chapter 14 Problem 6RQ: Into how many time constants is an exponential curve divided? … Get solutions Get solutions Get solutions done loading Looking for the textbook?

Source Image: advancedmathyoungstudents.com
Download Image
How to Find Particular Solutions to Differential Equations Involving Exponential Decay | Calculus | Study.com
Into how many time constants is an exponential curve divided? Expert Solution Trending now This is a popular solution! Step by step Solved in 2 steps See solution Check out a sample Q&A here Knowledge Booster Learn more about Analysis of Multiple Order System and Steady State Error Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application?

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
A Thorough Introduction to Holt-Winters Forecasting | by Lleyton Ariton | Analytics Vidhya | Medium
In an exponential function of the form f (x) = a*b^x, the initial value is usually taken to be the value of f (0), or “a”. The common ratio refers to the rate of change in an exponential function. In the form given above, the common ratio is “b”. For example, in the function f (x) = 2*3^x, the initial value is 2 and the common ratio is 3.

Source Image: medium.com
Download Image
Processes | Free Full-Text | Exponential Curve-Based Control Strategy for Auxiliary Equipment Power Supply Systems in Railways
A Thorough Introduction to Holt-Winters Forecasting | by Lleyton Ariton | Analytics Vidhya | Medium
The time is known to have an exponential distribution with the average amount of time equal to four minutes. X is a continuous random variable since time is measured. … The curve is: f(x) = 0.25e -0.25x where x is at least zero and m = 0.25. For example, f(5) = 0.25e −(0.25)(5) = 0.072. The postal clerk spends five minutes with the customers.
How Populations Grow: The Exponential and Logistic Equations | Learn Science at Scitable How to Find Particular Solutions to Differential Equations Involving Exponential Decay | Calculus | Study.com
Solutions for Chapter 14 Problem 6RQ: Into how many time constants is an exponential curve divided? … Get solutions Get solutions Get solutions done loading Looking for the textbook?